
stumbling into aerodynamics
Home Posts About Me

There are some terms and attributes that are important in analyzing how flows move. Some flows may have different complications which make it easier or more difficult to analyze than others.
An adiabatic process is one in which energy does not enter or leave the system. Another name for this is a closed or isolated system.
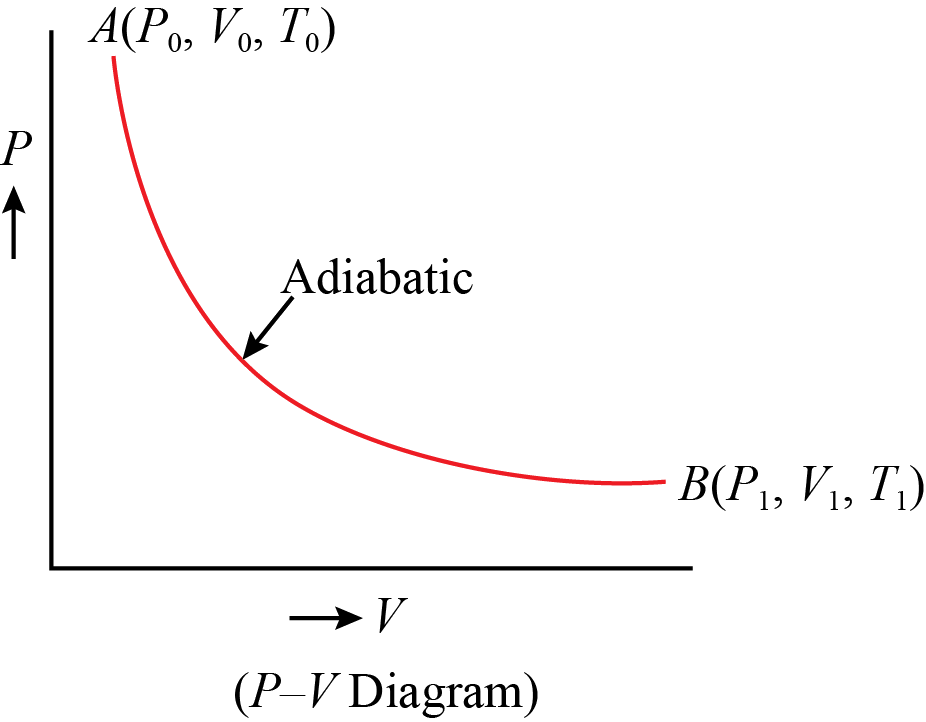
This graph illustrates an adiabatic reaction. In this diagram, \(P_0 V_0 = P_1 V_1\). The gas maintains its energy level. If the pressure rises, the velocity must fall. If this relationship is broken, the temperature of the control volume must change which means the average energy carries by each particle changes, and the energy in the control volume changes. If it is reasonable to assume that a process is adiabatic, it is best to do so because this makes analyzing the flow easier because it has no energy flux or flow.
Steadiness is another attribute that makes calculations easier. If the velocity of a flow doesn't change, the momentum flux doesn't change either. Many terms in the long sequences of equations will either be zero or constant.
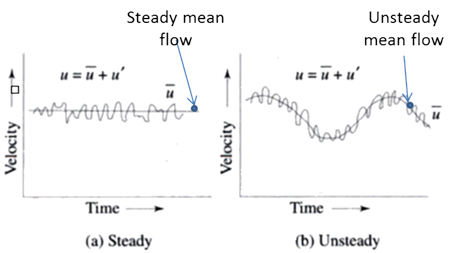
These graphs represent a steady flow. In the physical world there will be an amount of randomness, \(u'\), but is usually just ignored in favor of the average velocity, \(\bar{u}\).
An isentropic reaction is one which is easily suggested by its name: iso-, meaning same, and -tropic, pertaining to entropy. The reaction keeps the same entropy. This means the reaction can also be reversed. To be isentropic a reaction must first be adiabatic. This type of reaction has no flow of energy or matter.
--Aryn Harmon